How Does Cellular Activity Change When A Client With Hyperglycemia Receives Insulin?
The main function of the pancreas is to maintain salubrious blood sugar levels. Information technology is a large gland located backside the stomach. It produces insulin, glucagon, and other hormones. Diabetes occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the trunk does not use insulin properly (called insulin resistance).
Glucagon
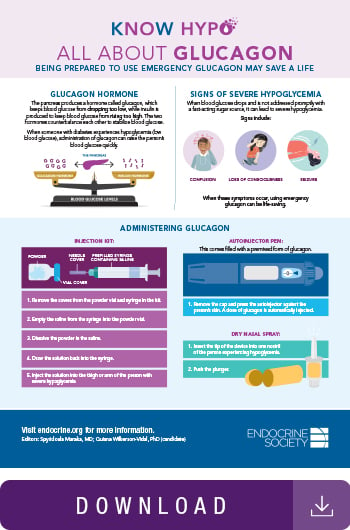
Glucagon is a hormone that works with other hormones and actual functions to control glucose levels in the blood. It comes from alpha cells found in the pancreas and is closely related to insulin-secreting beta cells, making it a crucial component that keeps the body'south blood glucose levels stable.
While glucagon keeps blood glucose from dropping too depression, insulin is produced to go on blood glucose from rising too high. The 2 hormones counterbalance each other to stabilize blood glucose. When blood glucose levels autumn besides low (low blood glucose), the pancreas pumps out more glucagon. This hormone helps claret glucose rising back up in multiple ways:
- Information technology causes the liver to convert stored glucose into a usable grade and then release it into the bloodstream. (A process called glycogenolysis.)
- Glucagon as well stops the liver from taking in and storing glucose, so more stays in the blood.
- Glucagon helps the trunk make glucose from other sources, such as amino acids.
When everything is working well, insulin moves glucose out of the blood and into the cells, where information technology is used for energy. Meanwhile, a complex feedback system within the body lets information technology know when no more glucagon is needed. In a nutshell, glucagon normally keeps blood glucose from dropping as well low. Insulin keeps it from ascension likewise high. The 2 hormones counterbalance each other.
Potential bug with glucagon part
Glucagon function is crucial to proper claret glucose levels, so problems with glucagon production will lead to problems with glucose levels. Low levels of glucagon are rare but are sometimes seen in babies. The chief outcome is low levels of claret glucose. The treatment is to inject the patient with glucagon. When the private has recovered sufficiently, eating carbohydrates volition then heighten the blood glucose levels even more.
High levels of glucagon are too rare but tin can occur when a patient develops a specific blazon of tumor in the pancreas. Patients with high levels of glucagon tin develop diabetes mellitus or experience unexpected weight loss.
Hypoglycemia and Glucagon
A mild instance of hypoglycemia may cause shakiness, headache, sweating, damp skin, or a pounding heartbeat. Claret glucose level falls to 54–69 mg/dL. Mild hypoglycemia can generally be treated by consuming xv grams of a fast-interim saccharide source, such as fruit juice, non-diet soda, difficult candies, or glucose tablets.
If hypoglycemia becomes severe, you may not be able to safely swallow nutrient or drink. By this point, the claret glucose level is less than 54 mg/dL—often below twoscore mg/dL. You may feel very confused, laissez passer out, or take a seizure. Without prompt handling, severe hypoglycemia may lead to a coma or even expiry.
Fortunately, severe hypoglycemia in a person with diabetes can be treated with prescription glucagon. Someone else will likely need to administer the glucagon, but this person does not accept to exist a wellness care professional. Relatives, friends, coworkers, and others tin can acquire to give glucagon.
Types of Emergency Glucagon
Injection Kit: A traditional injection kit contains a vial of powder (glucagon) and a syringe filled with saline (salt h2o).
Motorcar-injector Pen: A pre-mixed, gear up to use dose of glucagon. It is similar to the EpiPen used to treat serious allergic reactions.
Dry Nasal Spray: A (needle-free) nasal pulverization course of glucagon. It uses a plunger to spray into the nose, much similar a typical nasal spray.
What Happens After a Dose of Glucagon?
If you pass out due to astringent hypoglycemia, you volition usually regain consciousness within 15 minutes afterward receiving glucagon. In one case you are awake and able to swallow, your helper should give you a fast-interim sugar source. After that, eat a long-acting sugar source, such equally crackers and cheese or a sandwich with meat. In addition, call your health intendance provider right away. Your provider may have additional treatment advice.
If you remain unconscious xv minutes later receiving glucagon, your helper should administer one more dose of glucagon and call 911. Your helper should also call 911 if y'all wake up only are notwithstanding confused.
Side Furnishings of Emergency Glucagon
Possible side effects of glucagon treatment include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headache
- Temporary increment in heart rate
- Redness and swelling at the injection site.
For nasal glucagon, additional side effects may include:
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Reddish or watery eyes
- Itchy olfactory organ, eyes, or throat
If you are struggling with managing blood sugar, or chronic low blood saccharide levels, a number of factors could be causing your problem. Talk to your doctor about glucagon and whether or not it could exist a factor. Consider asking:
- Which treatments and lifestyle changes tin can assistance manage my diabetes?
- Is glucagon impacting my blood sugar levels?
- What can I practise to ameliorate glucagon levels?
- What should be my target blood glucose range?
- How can I ameliorate control blood saccharide levels?
- What can I do to increase my sensation of low blood glucose?
- How can I care for mild hypoglycemia to help continue information technology from becoming severe?
- Practise I need a glucagon prescription? If so, which product is all-time for my needs?
- Where tin people in my back up network notice training on how to give glucagon?
Insulin is Essential
Essential for life, the hormone insulin regulates many metabolic processes that provide cells with needed energy. Understanding insulin, what insulin does, and how it affects the body, is important to your overall health. Tucked abroad backside the stomach is an organ called the pancreas, which produces insulin. Insulin production is regulated based on blood sugar levels and other hormones in the trunk. In a healthy individual, insulin production and release is a tightly regulated procedure, allowing the trunk to residuum its metabolic needs.
What Does Insulin Do?
Insulin allows the cells in the muscles, fatty and liver to absorb glucose that is in the blood. The glucose serves as energy to these cells, or information technology can exist converted into fat when needed. Insulin also affects other metabolic processes, such every bit the breakdown of fat or protein.
Problems with Insulin Production or Use
The most common problem associated with insulin is diabetes. Diabetes occurs when the torso either does not secrete plenty insulin or when the body no longer uses the insulin information technology secretes effectively. Diabetes falls into two categories:
Type ane diabetes occurs when the pancreas cannot produce insulin sufficiently to meet its own needs. This commonly occurs in children, and while an verbal cause has non been found, many consider it to exist an autoimmune disease. Some symptoms of type one diabetes include tiredness, increased urination and thirst, and problems with vision.
Blazon 2 diabetes is more commonly associated with adults and lifestyle choices. People with type 2 diabetes will produce insulin but often not enough for their body's needs. They may also struggle to utilise the insulin they produce effectively. Patients may non know they have type 2 diabetes until they have an annual checkup, as symptoms tend to be mild until the disease has get severe.
When the trunk does not produce enough insulin or utilize it efficiently, claret carbohydrate levels build in the body. Also, the body's cells do non receive the energy they need from glucose, then the patient may struggle with fatigue. When the trunk turns to other tissue, similar fat or muscle, for free energy, weight loss may occur.
High blood sugars are a common symptom of diabetes, only patients who are treating their diabetes with insulin injections may inject too much insulin on occasion. This causes the body's cells to have likewise much glucose from the blood, leading to a low blood saccharide episode. Low blood sugar can cause defoliation, dizziness and fainting. Considering nervus cells rely entirely on glucose for energy, low blood carbohydrate can as well trigger a nervous system response.
If y'all suspect that y'all are struggling with insulin levels and production, your healthcare provider tin accept your insulin levels checked by an A1c blood test. If you are diagnosed with diabetes, yous volition need medical oversight to manage the condition. Consider asking:
- How can I manage blood sugar and insulin levels?
- What blazon of monitoring practise I need?
- What lifestyle changes can make blood sugar levels more stable?
- How tin I foreclose diabetes from developing if I am at take a chance but take not developed the illness?
Render to Hormones and Endocrine Function>>>
Source: https://www.endocrine.org/patient-engagement/endocrine-library/hormones-and-endocrine-function/pancreas-hormones
Posted by: woodsfambireett.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Does Cellular Activity Change When A Client With Hyperglycemia Receives Insulin?"
Post a Comment